41
Human exposure to PM10 microplastics in indoor air
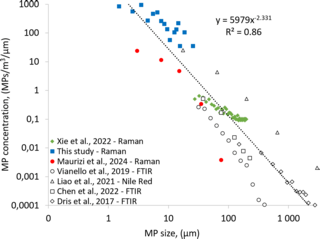
journals.plos.orgThe ubiquitous presence of airborne microplastics (MPs) in different indoor environments prompts serious concerns about the degree to which we inhale these particles and their potential impact on human health. Previous studies have mostly targeted MP in the 20–200 µm size range, which are less likely to efficiently penetrate into the lungs. In this study, we specifically investigate airborne, indoor suspended MPs in the inhalable 1–10 µm (MP1–10 µm) range in residential and car cabin environments, by using Raman spectroscopy. The median concentration of total suspended indoor MPs for the residential environment was 528 MPs/m3 and 2,238 MPs/m3 in the car cabin environment. The predominant polymer type in the residential environment was polyethylene (PE), and polyamide (PA) in the car cabin environment. Fragments were the dominant shape for 97% of the analyzed MPs, and 94% of MPs were smaller than 10 µm (MP1–10 µm), following a power size distribution law (the number of MP fragments increases exponentially as particle size decreases). We combine the new MP1–10 µm observations with published indoor MP data to derive a consensus indoor MP concentration distribution, which we use to estimate human adult indoor MP inhalation of 3,200 MPs/day for the 10–300 µm (MP10–300 µm) range, and 68,000 MPs/day for MP1–10 µm. The MP1–10 µm exposure estimates are 100-fold higher than previous estimates that were extrapolated from larger MP sizes, and suggest that the health impacts of MP inhalation may be more substantial than we realize.


Plastic in my lungs, plastic in my balls, plastic in my brain. I’m Barbie, without the dream house.
Filled with plastic; not fantastic!
This sounds like a song lyric.