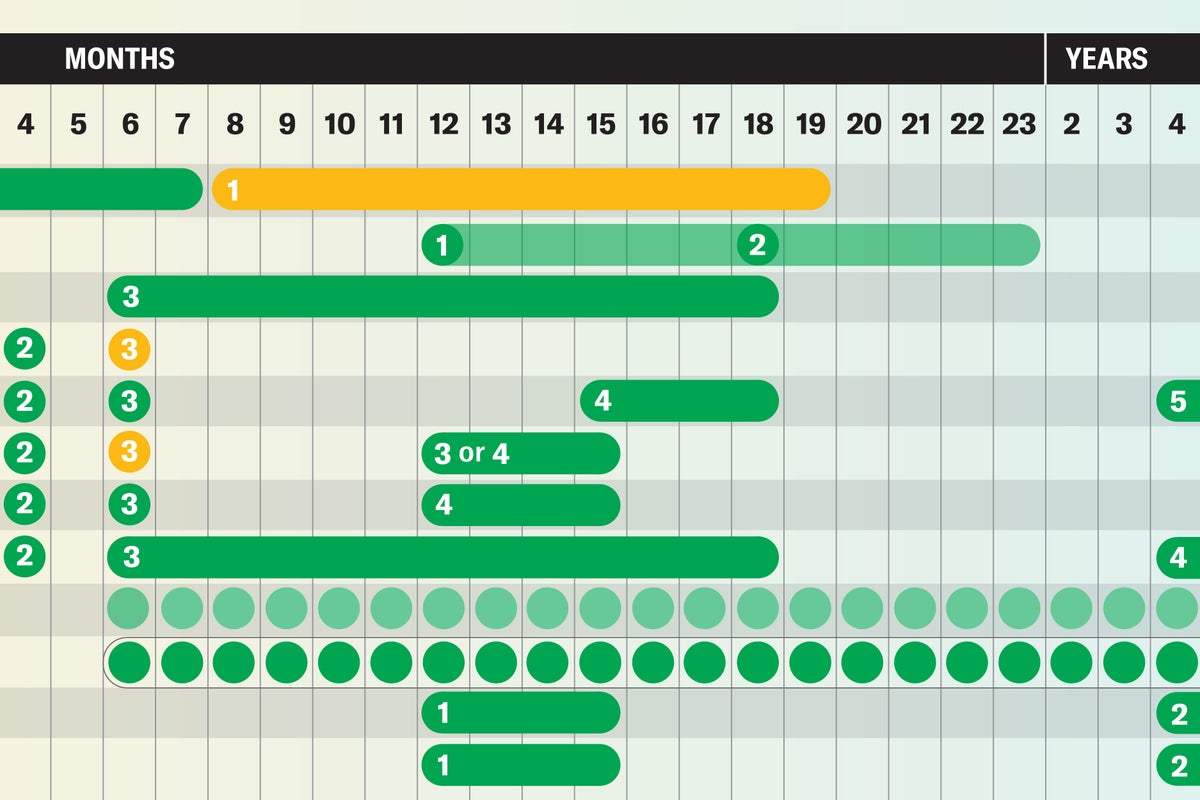
As a public resource, Scientific American has created graphics outlining the vaccines recommended by ACIP [the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices] as of its final meeting in 2024.
Vaccine recommendations have always been in flux as new products have been developed and continuing research has suggested better practices: The COVID pandemic required brand-new vaccines for a novel virus, for example. And in the U.S., the stunning success of the HPV (human papillomavirus) vaccine led to its recommendation for everyone aged 26 or younger, meanwhile the oral polio vaccine was discontinued in favor of the inactivated injected vaccine.
But traditionally, these decisions have been made by scientists based on solid research done within the confines of accepted ethical practices. These principles mean, for example, that a vaccine’s side effects are carefully monitored and evaluated against its immune benefit and that potential replacement vaccines are tested against their predecessors, not—as Kennedy has proposed—an inert placebo that would leave people vulnerable to an infection that doctors already have the tools to combat.
Kennedy’s decision to replace ACIP wholesale and the comments he has made about deviating from standard vaccine policymaking practice suggest that new recommendations won’t be backed by established vaccine science—hence our reproduction of the vaccine recommendations as of the end of 2024.
The chart is cutoff.
the “chart” is just the thumbnail for the submission, so yeah; you have to actually click through, since that’s the point of a link aggregator